Acanthamoeba: Biology and Pathogenesis
|
Author: Naveed Khan Published: 2009 ISBN: 978-1-904455-43-1 Everything that is known about Acanthamoeba is critically reviewed and divided into easy-to-follow sections. The current state of research on genomics, molecular and cellular biology, life cycles, geographical distribution, role in ecosystem, morphology, motility, phylogenetics, genotyping, metabolism, regulation of morphogenesis, host-parasite interactions, the molecular and immunological basis of pathogenesis, methods of transmission, epidemiology, clinical manifestation, diagnosis, treatment, new target development and drug resistance, and much more. read more ... |
Figure from: Acanthamoeba Biology and Pathogenesis
Full details of this book at Acanthamoeba. More figures at Acanthamoeba Figures.
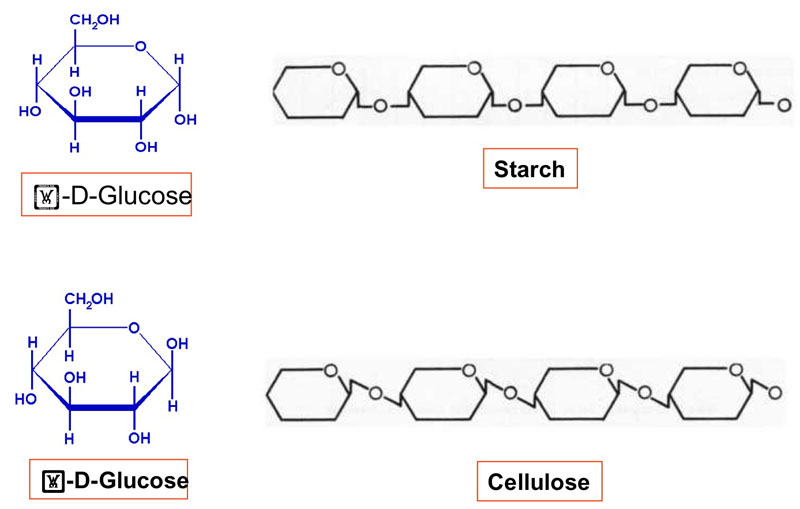
Section B. Figure 7. The structure of starch (polymer of alpha-glucose) and cellulose (polymer of beta-glucose) are similar, i.e., formed by long glucose unit chains. Glycogen (polymer of alpha-glucose) however has a longer chain and is more highly branched as shown in Section A, figure 9B. The orientation of the units in cellulose results in a linear chain, which allows other chains to closely pack by hydrogen bonding. This increases the strength of cellulose (compared with starch) and accounts for its low solubility in water, hence it can be used to make clothes, ropes etc.
Further reading at Acanthamoeba. More figures at Acanthamoeba Figures.



